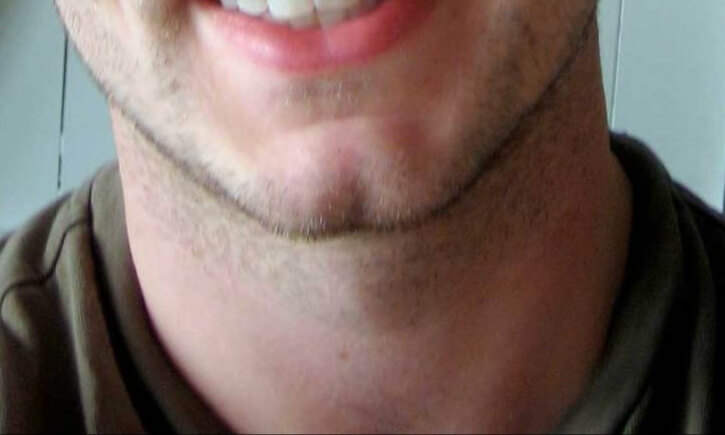
The terms cleft chin, chin cleft, dimple chin, or chin dimple, refer to a dimple on the chin.
What is a Cleft Chin?
Simple definition:
Fancy definition:
Specifically, the chin fissure follows the fissure in the lower jaw bone that resulted from the incomplete fusion of the left and right halves of the jaw bone, or muscle, during the embryonal and fetal development. For other individuals, it can develop over time, often because one half of the jaw is longer than the other, leading to facial asymmetry.
A cleft chin is an inherited trait in humans, where the recessive gene causes the cleft chin, while the dominant presents without a cleft. However, it is also a classic example for variable penetrance with environmental factors or a modifier gene possibly affecting the phenotypical expression of the actual genotype. Cleft chins are common among people originating from Europe, the Middle East and India.
Curtesy of Wikipedia
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chin#Cleft_chin
What is a Widow’s Peak?
Simple definition:
V-shaped growth of hair toward the center of the forehead, especially one left by a receding hairline in a man.
Fancy definition:
A widow’s peak is a V-shaped point in the hairline in the center of the forehead. Hair growth on the forehead is suppressed in a bilateral pair of periorbital fields. Without a widow’s peak, these fields join in the middle of the forehead so as to give a hairline that runs straight across. A widow’s peak results when the point of intersection on the forehead of the upper perimeters of these fields is lower than usual.
Curtesy of Wikipedia
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Widow%27s_peak

What are Dimples?
Simple definition:
A dimple is a small natural indentation in the flesh on a part of the human body, most notably in the cheek or on the chin.
Fancy definition:
Dimples may be caused by variations in the structure of the facial muscle known as zygomaticus major. Specifically, the presence of a double or bifid zygomaticus major muscle may explain the formation of cheek dimples. This bifid variation of the muscle originates as a single structure from the zygomatic bone. As it travels anteriorly, it then divides with a superior bundle that inserts in the typical position above the corner of the mouth. An inferior bundle inserts below the corner of the mouth.
Curtesy of Wikipedia
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dimple

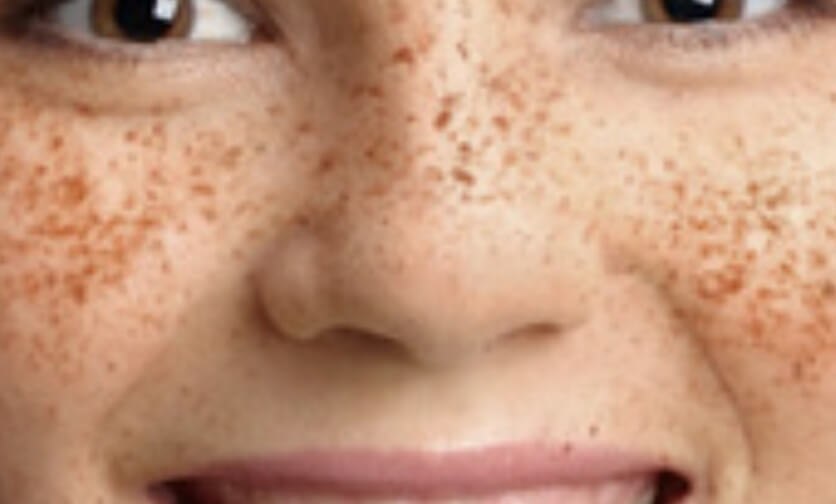
What are Freckles?
Simple definition:
Freckles are small brown spots on your skin, often in areas that get sun exposure. Freckles typically don’t raise off the skin. In most cases, freckles are harmless.
Fancy definition:
The presence of freckles is related to rare alleles of the MC1R gene, though it does not differentiate whether an individual will have freckles if they have one or even two copies of this gene. Also, individuals with no copies of the MC1R do sometimes display freckles. Even so, individuals with a high number of freckling sites have one or more of variants of the MC1R gene. Of the variants of the MC1R gene Arg151Cys, Arg160Trp, and Asp294His are the most common in the freckled subjects. The MC1R gene is also associated with red hair more strongly than with freckles. Most red-haired individuals have two variants of the MC1R gene and almost all have one. The variants that cause red hair are the same that cause freckling. Freckling can also be found in areas, such as Japan, where red hair is not seen. These individuals have the variant Val92Met which is also found in Caucasians, although it has minimal effects on their pigmentation. The R162Q allele has a disputed involvement in freckling.
The variants of the MC1R gene that are linked with freckles started to emerge in the human genotype when humans started to leave Africa. The variant Val92Met arose somewhere between 250,000 and 100,000 years ago, long enough for this gene to be carried by humans into central Asia. Arg160Trp is estimated to have arisen around 80,000 years ago while Arg151Cys and Asp294His have been estimated to arise around 30,000 years ago. The wide variation of the MC1R gene exists in people of European descent because of the lack of strong environmental pressures on the gene. The original allele of MC1R coded for dark skin with a high melanin content in the cells. The high melanin content is protective in areas of high UV light exposure. The need was less as humans moved into higher latitudes where incoming sunlight has lower UV light content. The adaptation of lighter skin is needed so that individuals in higher latitudes can still absorb enough UV for the production of vitamin D. Freckled individuals tend to tan less and have very light skin, which would have helped the individuals that expressed these genes absorb vitamin D.

What is a Free Earlobe?
Simple definition:
Free Earlobes: Free earlobes are the most common form of lobes found. This type of earlobe is often large and hangs below the point of attachment to the head.
Attached Earlobes: These types of earlobes are not rare but are also not commonly found. Earlobes of such type are small in size and do not have hangs.
Fancy definition:
Earlobes average about 2 centimeters long and elongate slightly with age. Although the “free” vs. “attached” appearance of earlobes is often presented as an example of a simple “one gene – two alleles” Mendelian trait in humans, earlobes do not all fall neatly into either category; there is a continuous range from one extreme to the other, suggesting the influence of several genes.
Curtesy of Wikipedia & News Medical Life Sciences
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Earlobe
https://www.news-medical.net/health/Genetics-of-Earlobes.aspx

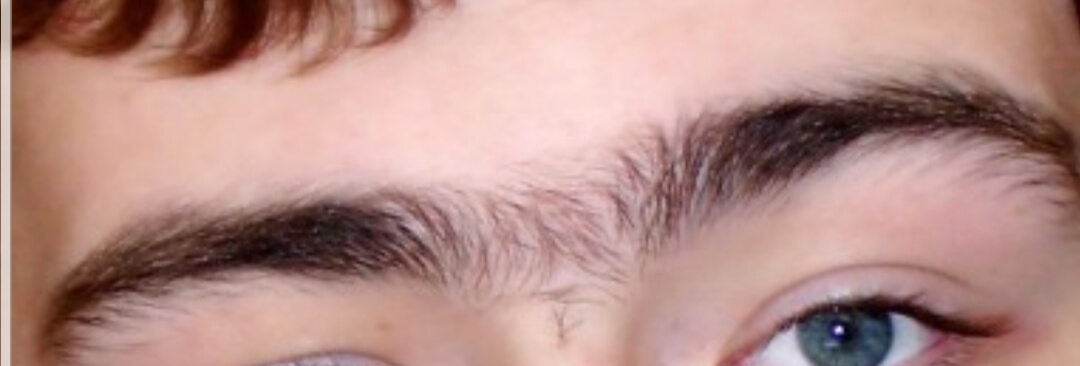
What are Connected Eyebrows?
Simple definition:
A unibrow or connected eyebrow is a single eyebrow created when the two eyebrows meet in the middle above the bridge of the nose.
Fancy definition:
The hair above the bridge of the nose is usually of the same color and thickness as the eyebrows, giving the appearance that they converge to form one uninterrupted line of hair.
The unibrow is a recessive genetic trait. It is associated with the PAX3 gene.