There are some common tests that may be recommended from your health professionals during the pregnancy such as genetic screening, first trimester, second trimester, fetal monitoring, Amniocentesis and CVS . These tests are designed to provide important information about the health of the fetus.
Look at some common first trimester tests below:
First trimester tests
There are some tests which are conducted in the first trimester include:
Ultrasound for fetal nuchal translucency (NT)
This screening test uses ultrasound for examining the area at the back of the fetal neck to check the increased fluid or thickening.
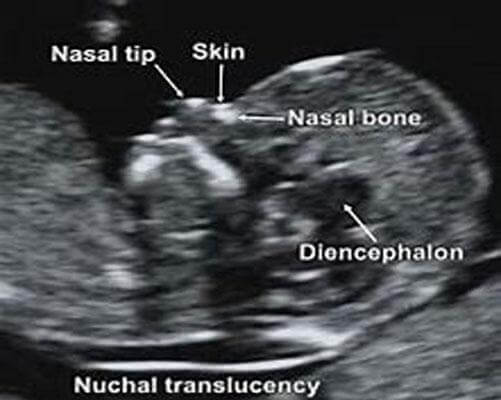
Ultrasound for fetal nasal bone determination
In some cases, the nasal bone may not be visualized with certain chromosome abnormalities such as Down syndrome. This screening test is performed by ultrasound between the 11 and 13 weeks of pregnancy.
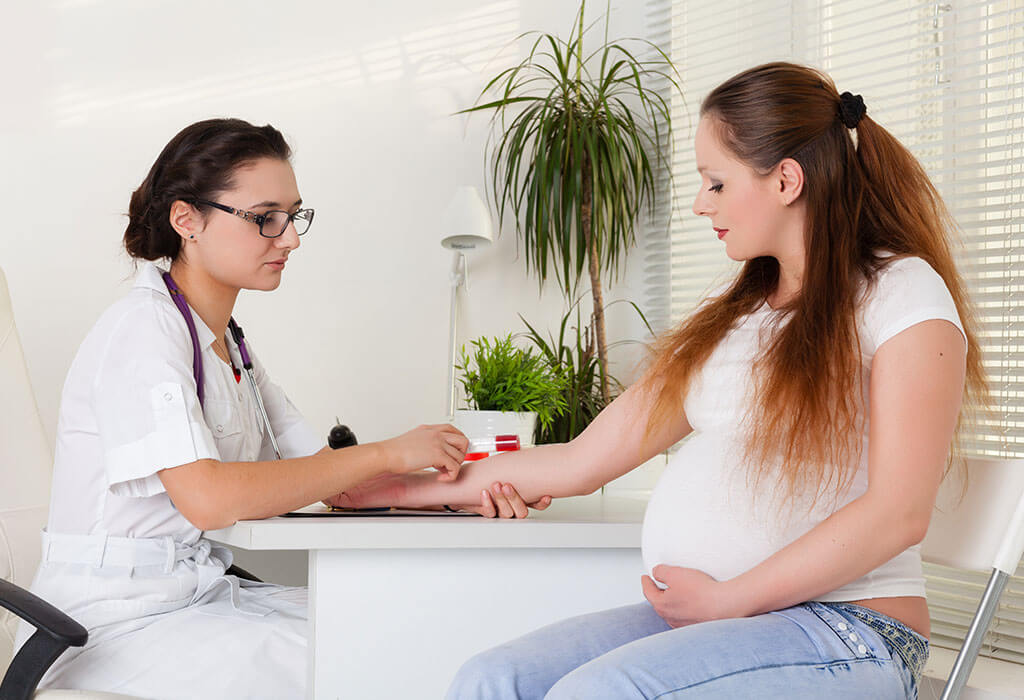
Maternal serum (blood) tests
These blood tests measure two substances found in the blood of a pregnant woman as mentioned below:

Pregnancy-associated plasma protein A
A protein is produced by the placenta in early pregnancy. If there are abnormal levels of protein A then there are increased risks of chromosomal abnormalities.
Human chorionic gonadotropin
This hormone is produced by the placenta and in case of abnormal levels, there will be an increased risk of any particular chromosomal abnormality.
You can take the help of DNA testing in Dallas for the first trimester checkups. Here, you can also ask for various other DNA testing such as paternity testing, sibling, face recognition, forensics, immigration testing, etc.
Some common tests are done during the first trimester of pregnancy.
Following the initial appointment, you should anticipate having your blood pressure, weight, and urine examined at each visit until the delivery. Preeclampsia, or dangerously elevated blood pressure, and gestational diabetes are among the conditions that these tests can detect.
a number of variables such as your age, health, medical history in your family, and other factors, you may be offered additional tests throughout the first trimester of pregnancy. These may consist of:
Ultrasound: This non-invasive, safe procedure creates pictures of the baby’s location and form using sound waves. It can be done as part of the first trimester screening at weeks 11–14, or early in the trimester to date the pregnancy. Several ultrasounds may be performed on women with high-risk pregnancies throughout the first trimester.
Non-invasive prenatal screening (NIPS) and cell-free DNA testing: This blood test looks for traces of the mother’s fetal DNA. It can be performed as early as 10 weeks into the pregnancy to determine whether the fetus is at risk for a chromosomal abnormality. It’s not a test for diagnosis. Another test is required to confirm or rule out the diagnosis if the findings are abnormal. Usually, expectant women who are older or who have given birth to a child with a chromosomal issue are offered it since they are at a higher risk.
Chorionic villus sampling (CVS): This procedure examines placental cells to detect any chromosomal abnormalities (like Down syndrome). If a baby is going to be born with a certain chromosomal condition, it can be determined with certainty between weeks 10 and 13.
Which Other Exams Could Be Possible?
During a woman’s pregnancy, medical professionals may prescribe further tests depending on risk factors, her personal medical history, and the medical histories of her partner. If your child is susceptible to any inherited diseases, it is imperative that you consult a genetic counsellor.
Among the available screening or diagnostic procedures are those for:
- thyroid disease
- toxoplasmosis
- hepatitis C
- Tay-Sachs disease
Choose Clarity with Our DNA Test.
Get Accurate Answers With our Test!.
-
- Accurate
- Quick Result
- Private and Secure
- Affordable

Why are ultrasounds performed during the first trimester?
Pregnancy ultrasounds can be performed for several reasons and at different dates.
- To determine the deadline (this is the most precise method available)
- to count the number of fetuses and recognize the placental anatomy.
- to identify a miscarriage or ectopic pregnancy
- To investigate other pelvic anatomy and the uterus
- to find anomalies in the fetus (in some circumstances)







Leave a Reply
Your email is safe with us.
You must be logged in to post a comment.